Google released Chrome 112, a new stable version of the company's web browser, to the Stable channel. Chrome 112 is a security update first and foremost, but it does include new features and changes as well.
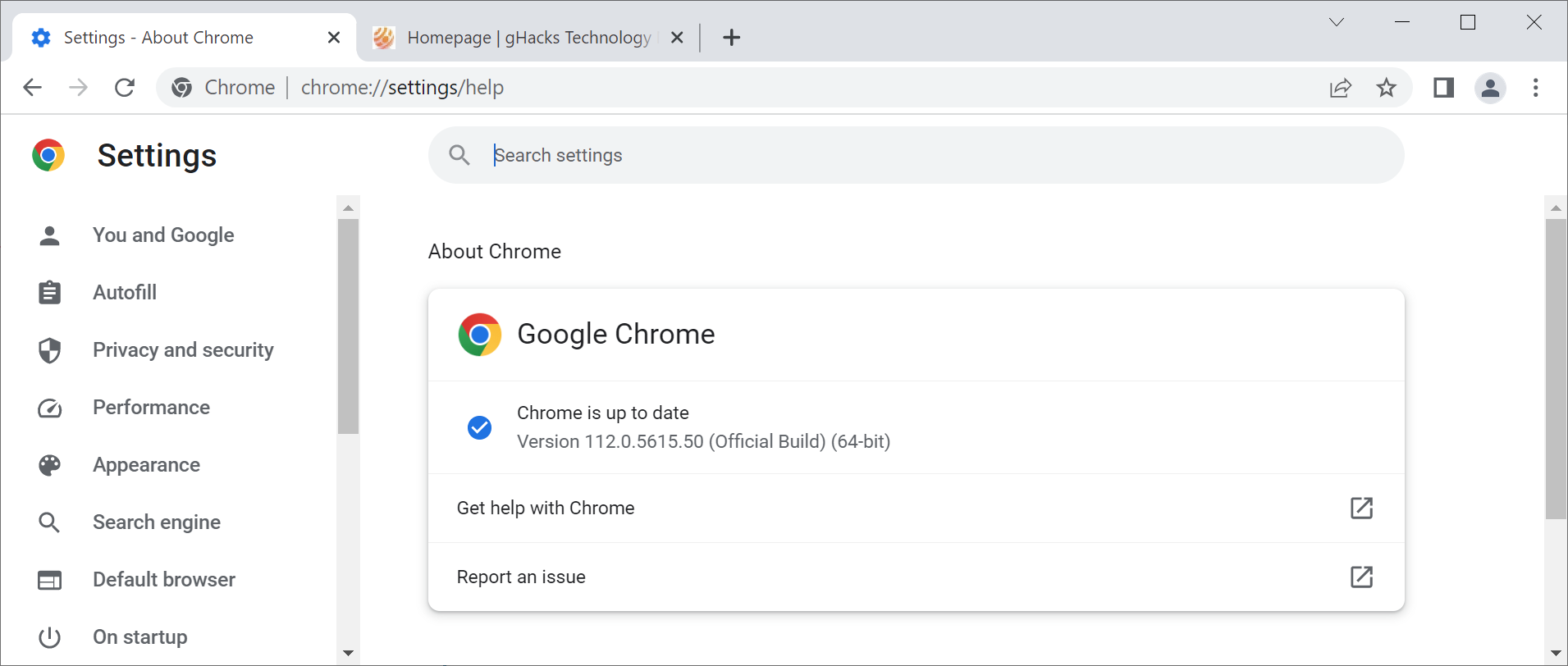
Chrome users may load chrome://settings/help in the browser's address bar to display the installed version and run a check for updates. It should find the new Chrome update, if not installed already, and download it. A restart of the browser is required and the new Chrome version is launched.
The following versions should be listed after the update:
- Chrome for Linux and Mac: 112.0.5615.49
- Chrome for Windows: 112.0.5615.49 or 112.0.5615.50
- Chrome for Android: 112.0.5615.47 or 112.0.5615.48
- Chrome for iOS: 112.0.5615.46
Chrome 112
Google Chrome 112 is a security update for all platforms. It addresses 16 different security issues in the web browser. Google lists externally reported security vulnerabilities on the official Chrome Releases website. The severity ratings of the issues are high, medium and low. They address a wide range of security-related issues, including heap buffer overflow, user after free, out of bounds or insufficient policy enforcement issues.
Google makes no mention of exploits in the wild. While that is reassuring, it is still suggested to update to the latest Chrome version as soon as possible to protect the browser against potential attacks targeting the security issues.
The Chrome Status page for Chrome 112 lists developer related changes for the most part:
- Deprecate the `document.domain` setter. (Deprecated)
- Add optional submitter parameter to FormData constructor
- CSS animation-composition property
- CSS Nesting
- RegExp v flag with set notation + properties of strings
- “Reload this page” infobar no longer shown if top-level frame is observing permission changes
- WebAssembly Tail Call
- WebGLContextEvent on Web Workers
- Add containerName and containerQuery, update conditionText (behind flag)
- background-blur (behind flag)
- Deprecate non-standard `shadowroot` attribute for declarative shadow DOM (behind flag)
- FedCM: Auto re-authentication (behind flag)
- APIPayment handler minimal header UX (behind flag)
- “Reload this page” infobar no longer shown if top-level frame is observing permission changes (behind flag)
- WebAssembly Garbage Collection (WasmGC) (Origin trial)
- [WebRTC] Unship deprecated "track" and "stream" stats from getStats() (Origin trial)
Check out the website for additional information on these. Chrome users may notice a few changes as well. One of them is the retirement of Chrome apps. These apps do not work anymore in Chrome 112. Google decided to retire the technology in favor of Progressive Web Apps (PWAs).
Chrome for iOS will automatically upgrade mixed-content to HTTPS whenever possible. The browser did block mixed content previously. Also on iOS is the ability to add websites and PWAs to the home screen.
Also starting in Chrome 112 is an addition to the browser's Safety Check feature. It will no revoke site permissions of sites that have not been visited for a while. Google describes the feature in the following way: "
Starting with Chrome 112, safety check includes auto-revocation of unused site permissions on Chrome. Chrome resets permissions from sites that users have not visited for a while. Chrome revokes permissions automatically and offers options to opt out or re-grant. Permissions granted by enterprise policies are not affected."
Chrome admins and users on Android may load chrome://policy/logs to troubleshoot Enterprise policies.
Last but not least, chrome's HTTP Only Mode includes a new policy that supports force_enabled. It enables the Always use secure connection option that is found under chrome://settings/security.
Thank you for being a Ghacks reader. The post Google Chrome 112 fixes 16 unique security issues appeared first on gHacks Technology News.
0 Commentaires